what does transcription result in|Stages of transcription : Pilipinas Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are . The loop is much like before: build super as fast as possible then pop it during times of distress. With Unbreakable, we’re able to build it even faster, both with Ursa and mods like Ashes to Assets and Firepower, which activate on any kill with the shield blast. Pairing this with Buried Bloodline is highly recommended, as Devour’s grenade .Subscribe to Morning Kombat with Luke Thomas and Brian Campbell for the best analysis and in-depth news, including instant analysis of Davis vs. Garcia live from Las Vegas at the conclusion of the .
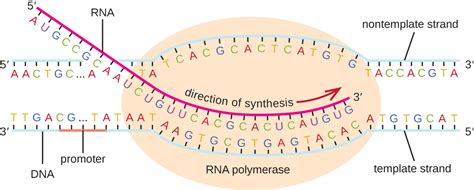
what does transcription result in,Transcription, the synthesis of RNA from DNA. Genetic information flows from DNA into protein, the substance that gives an organism its form. .
Transcription is the process in which a DNA sequence is transcribed into an RNA molecule with the help of enzyme RNA polymerase. One of the .
Last Updated: April 7, 2019. Transcription Definition. Transcription refers to the first step of gene expression where an RNA polymer is created .
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are . Transcription is the process where a specific segment of DNA is used as a template and copied into an RNA molecule. This synthesis is carried out by an enzyme known as RNA polymerase. The .
The process of transcription begins when an enzyme called RNA polymerase (RNA pol) attaches to the template DNA strand and begins to catalyze production of complementary RNA. Polymerases are.
Transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA safely and stably stores genetic .In transcription, an RNA polymerase uses the template DNA strand of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand. RNA polymerases use ribose nucleotide triphosphate (NTP) precursors, .The RNA polymerase is the main enzyme involved in transcription. It uses single-strand DNA to synthesize a complementary RNA strand. The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the . The cell cycle consists of four phases-G1, S, G2, and M. During the G1 phase, cells grow and produce material like nucleotide precursors as preparation for DNA replication in the S-phase. . The Steps of Transcription. Some 50 different protein transcription factors bind to promoter sites, usually on the 5′ side of the gene to be transcribed.; An enzyme, an RNA polymerase, binds to the complex of transcription factors.; Working together, they open the DNA double helix. The RNA polymerase proceeds to read one strand moving .

Transcription factors are proteins that help turn specific genes "on" or "off" by binding to nearby DNA. Transcription factors that are activators boost a gene's transcription. Repressors decrease transcription. Groups of transcription factor binding sites called enhancers and silencers can turn a gene on/off in specific parts of the body. Steps of Transcription. The process of Transcription takes place in the cytoplasm in prokaryotes and in nucleus in eukaryotes. It uses DNA as a template to make an RNA (mRNA) molecule. During transcription, a strand of mRNA is made that is complementary to a strand of DNA. Figure 1 shows how this occurs.
Updated on December 10, 2021. DNA transcription is a process that involves transcribing genetic information from DNA to RNA. The transcribed DNA message, or RNA transcript, is used to produce proteins. DNA is housed within the nucleus of our cells. It controls cellular activity by coding for the production of proteins.what does transcription result in These results suggest that transcriptional amplification reduces rate-limiting constraints for tumor cell growth and proliferation. Mutations in the Mediator coactivator complex have recently been implicated in the development of various tumors. Uterine leiomyomas, or fibroids, are benign tumors that affect millions of women.
Step 1: Initiation. Initiation is the beginning of transcription. It occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a region of a gene called the promoter. This signals the DNA to unwind so the enzyme can ‘‘read’’ the bases in one of the DNA strands. The enzyme is now ready to make a strand of mRNA with a complementary sequence of bases.Steps of Transcription. Transcription takes place in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. The steps are illustrated in Figure below.. Initiation is the beginning of transcription. It occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a region of a gene called the promoter.This signals the DNA to unwind so the enzyme can ‘‘read’’ the bases .What isn't shown in the diagram is that each kinase phosphorylates the next until one phosphorylates a transcription factor. In most cases, the activated transcription factor then transcribes a section of DNA that codes for a protein in response to the original ligand binding. Thus, the synthesis of this protein is the "response" mentioned.
Definition. Transcription, as related to genomics, is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene’s DNA sequence. This copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the gene’s protein information .
Common Lab Tests for the MT. The average MT can edit or transcribe many reports in the course of a workday. It would not be a stretch of the imagination to estimate 20 to 50 reports per day, at least. It all depends .Transcription and mRNA processing. Transcription involves rewriting genetic information from DNA to mRNA, with RNA polymerase playing a crucial role. In eukaryotic cells, DNA to mRNA transcription occurs within the nucleus, producing pre-mRNA. This pre-mRNA undergoes processing, including the addition of a 5' cap, a poly-A tail, and splicing .
This scanning mechanism does not involve transcription of the DNA between the TATA and initiation site (Khaperskyy et al. 2008). Since the cost of disrupting a DNA base pair is ∼2 kcal/mol, there is a significant energetic cost of unwinding 10–70 bp. . What mechanisms result in transcription stimulation? (2) How is formation of .
transcription / DNA transcription. Transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA safely and stably stores .
Initiation of transcription begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter. Transcription requires the DNA double helix to partially unwind such that one strand can be used as the template for RNA synthesis. The region of unwinding is called a transcription bubble. Figure 3.

Key points: When an RNA transcript is first made in a eukaryotic cell, it is considered a pre-mRNA and must be processed into a messenger RNA ( mRNA). A 5' cap is added to the beginning of the RNA transcript, and a 3' poly-A tail is added to the end. In splicing, some sections of the RNA transcript ( introns) are removed, and the remaining .
The authors examined the signaling factor β-catenin, which does not contain a DNA binding domain and is thought to be recruited to super enhancers by transcription factors of the T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor (TCF/LEF) family. . is that there is a difference in specific binding which results in transcriptional activation vs .
what does transcription result in|Stages of transcription
PH0 · transcription / DNA transcription
PH1 · What Is Transcription?
PH2 · Transcription: an overview of DNA transcription (article)
PH3 · Transcription (biology)
PH4 · Transcription
PH5 · Stages of transcription
PH6 · DNA Transcription
PH7 · Biochemistry, Replication and Transcription
PH8 · 10.2: Overview of Transcription